[Introduction]The application of CAN bus is more and more extensive. How can engineers quickly locate faults under different working conditions? This article will introduce the troubles caused by CAN network faults, as well as several methods for quickly locating faults, which can help you quickly make judgments and make selections.
The future development of new energy vehicles
Now concepts such as big data, the Internet of Things, and smart homes have penetrated into thousands of households and into the future of the automotive industry. A typical example is the automated driving of cars.
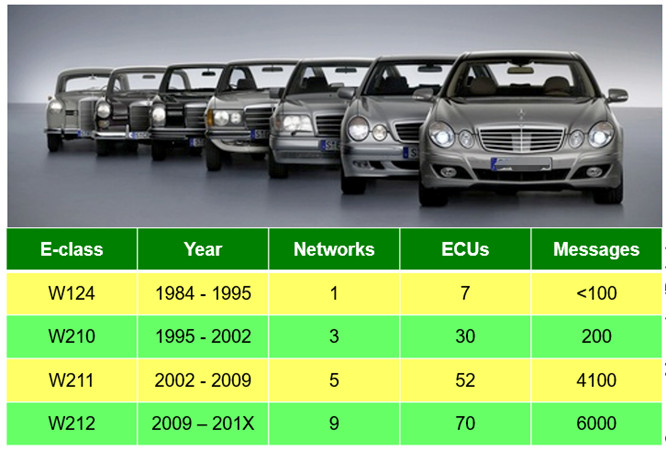
Figure 1 Changes in vehicle traffic with years
As shown in Figure 1, as the functions implemented by the vehicle gradually increase, the network of the entire vehicle becomes more and more complex, and the amount of communication that needs to be carried out also skyrockets. In order to face the surge in data transmission, in the future, new energy vehicles will gradually upgrade from the existing CAN bus communication to CAN FD to cope with this change.
Fault common phenomenon
When the CAN bus fails or the data transmission is abnormal, there are often a variety of strange failure phenomena, such as:
● The dashboard Display is abnormal, keeps jumping, and the actual value;
● The vehicle cannot be started normally and cannot be extinguished after starting;
● Some Electronic control systems of the vehicle malfunction;
● The motor rotates abnormally, and the power supply changes greatly.
CAN bus fault location
Most of the fault problems of the CAN bus are caused by problems in the transmission of the physical layer. Therefore, in order to locate the fault of the CAN bus, it is necessary to analyze the messages of the CAN bus.
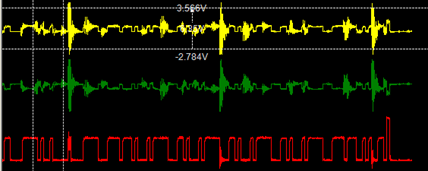
Figure 2 CAN bus abnormal state waveform diagram
A common problem in new energy vehicles is interference. As shown in Figure 2, the waveform of a vehicle communication captured by our CAN bus analyzer is used. When locating the CAN bus fault, the cause of abnormal interference should be determined according to the waveform.
It can be seen that abnormal common-mode signals are superimposed on CAN_H and CAN_L, so FFT spectrum analysis is performed for abnormal common-mode signals to help users quickly locate common-mode interference frequencies.
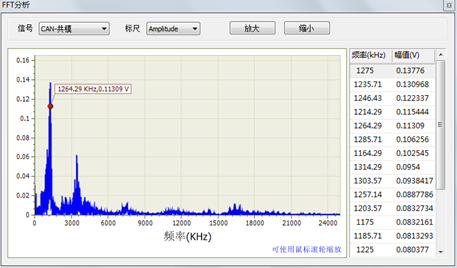
Figure 3 FFT analysis results
Figure 3 shows the FFT analysis results. It can be seen that the interference is mainly concentrated around 1264KHz, which proves that there is a node in the CAN bus network that generates a signal of this frequency, and the crosstalk enters the CAN bus network, resulting in bus communication. abnormal.
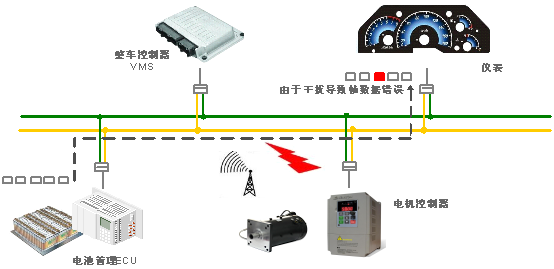
Figure 4 CAN bus network example diagram
Figure 4 shows an example diagram of the CAN bus network. After testing each node, it is found that the common mode interference frequency is consistent with the inverter frequency. It is finally determined that the communication abnormality is caused by the crosstalk of the inverter signal entering the bus.
Interference elimination method
After we have determined the cause of the failure of the CAN bus, we need to eliminate the interference, then the commonly used anti-interference solutions will be introduced below.
1. Add isolation module
Interference not only affects the signal, but also causes the board to crash or burn, so the isolation of the interface and the power supply is the first step in anti-interference. The main purpose of isolation is to prevent ground flow from burning the board and limit the magnitude of interference. As shown in Figure 5, when not isolated, the ground potentials of the two nodes are inconsistent, resulting in a return current and a common mode signal. The anti-common mode interference capability of CAN is -12~7V, and an error occurs if the difference exceeds this value. The common mode difference exceeds ±36V, which will burn the transceiver or the Circuit board. After the CTM isolation module is added, the ground return flow is isolated, the interference amplitude is limited, and the bus anti-interference is increased.
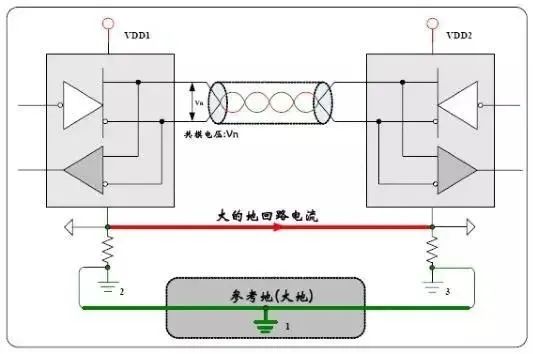
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of differential anti-interference
2. Increase the degree of twisting
In order to improve the anti-interference ability of CAN bus, CANH and CANL differential transmission are adopted. The effect is that after encountering interference, it can be “same as above”, and finally the differential value of CANH-CANL remains unchanged. As shown in Figure 6.
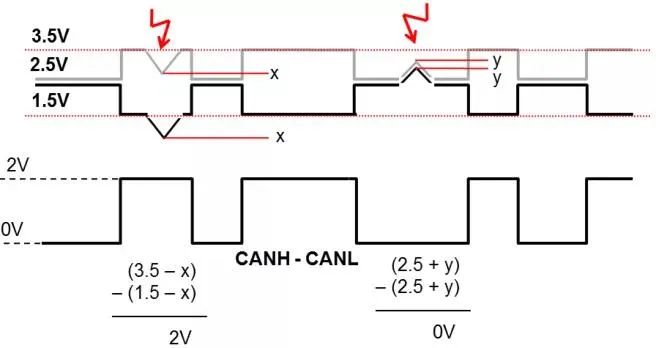
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of differential anti-interference
CANH and CANL should be closely twisted together, usually only 33 twists/meter of twisted pair, and in the case of strong interference, the twisted pair should be 45-55 twists/meter to achieve better anti-interference effect.
3. The CAN line ensures the shielding effect and correct grounding
The CAN wire with a shielding layer can well resist the interference of the electric field, which means that the entire shielding layer is an equipotential body to avoid the interference of the CAN wire. As shown in Figure 7, for a standard shielded twisted pair, CANH and CANL are wrapped by aluminum foil and oxygen-free copper wire shielding net, as shown in Figure 7. It should be noted that in the connection with the connector, cables shorter than 25mm are allowed in the connection part without twisting. A better CAN shielded wire has 2 layers of shielding layers, which is called a double-layered shielded wire. The CAN_GND of the inner layer is connected to the ground of the CAN transceiver, and the shield of the outer layer is connected to the ground of the casing.

Figure 7 Shielded twisted pair
4. Use CAN bridge
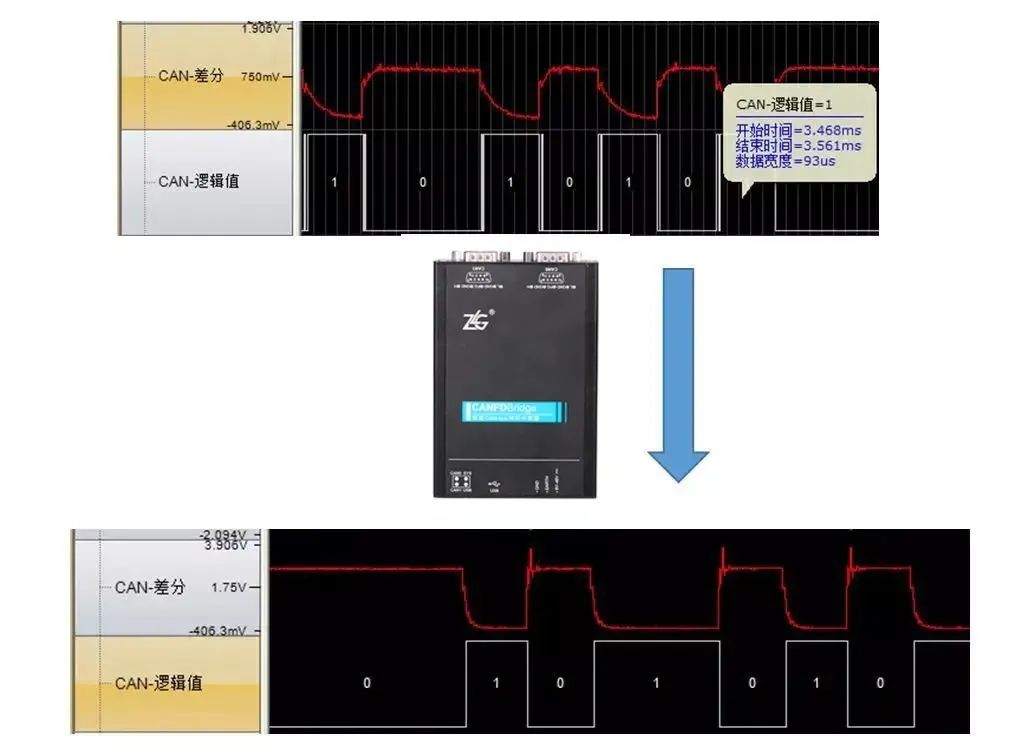
Figure 8 Schematic diagram of CAN bridge anti-interference
As can be seen from Figure 8, before the waveform passes through the CAN bridge, due to the large bus capacitance, the falling edge becomes very slow, forming a sickle shape, which easily leads to bit sampling errors. After passing through the CAN bridge, the message waveform is reshaped and re-sent. It can be seen that the overall condition of the waveform is good, which can ensure the normal sending and receiving of the message.
test solution
This is the iceberg model of the CAN bus. At present, engineers only focus on the surface part: whether the transmission is normal and the protocol analysis, but there are many influencing factors at the bottom, such as stress test, bus delay, etc.

Figure 9 CAN bus iceberg model
In order to ensure the normal communication of the CAN bus, it is necessary to carry out a variety of tests during the research and development test to increase the robustness and consistency of the CAN bus and ensure the normal communication.
At present, ZLG Zhiyuan electronics’ first CANFD bus analysis and test product has been officially released. ZPS-CANFD, as the second-generation bus development auxiliary tool, can be applied to CANFD, CAN, LIN bus measurement and test instruments, and can provide industry users with reliable multiple Bus test analysis platform.
1. Meet CAN FD, CAN, LIN multi-bus test analysis
ZPS-CANFD perfectly matches the development of automotive Electronic platforms, focusing on the measurement and testing of CANFD, CAN, and LIN buses of intelligent connected vehicles, and can efficiently complete the multi-level comparative analysis of buses, from physical layer analog signals, digital logic signals, data links. Road layer, protocol layer, application layer analysis and comparison display.
2. Powerful software eye diagram to clearly find signal distortion
The deeply customized software eye diagram based on the characteristics of the bus signal can directly observe the degree of signal distortion, evaluate the amplitude of the CANFD bus, and further judge whether the bus transmission conforms to the standard and exists risks.
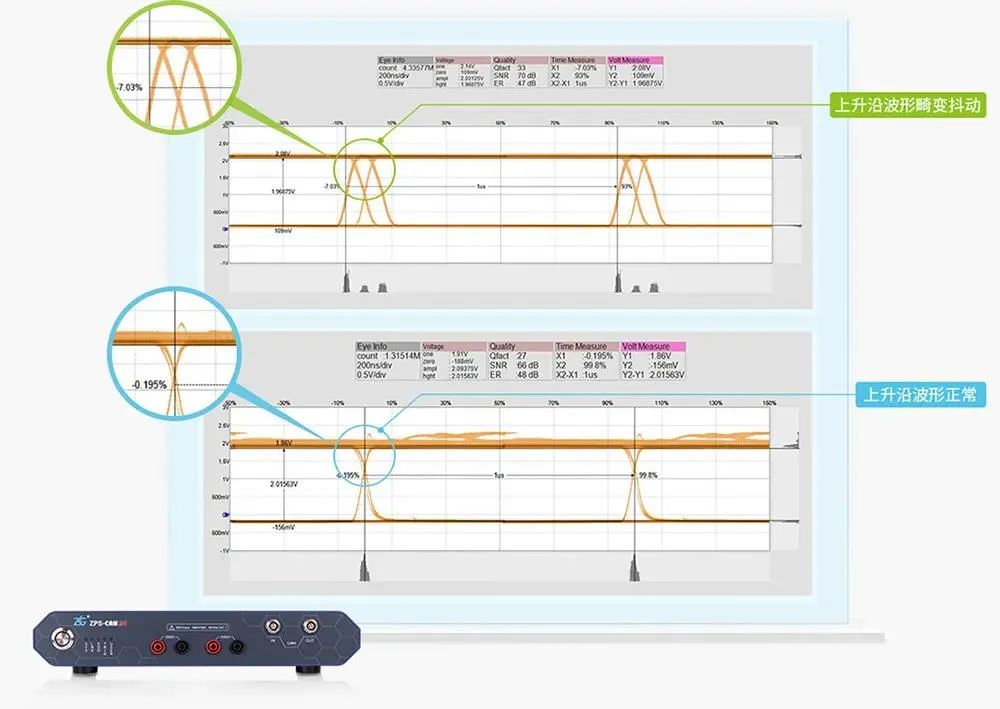
3. Support signal quality analysis, multi-dimensional evaluation of node signal characteristics
ZPS-CANFD bus analyzer analyzes and evaluates CANFD bus signal quality from multi-dimensional parameters such as amplitude, disturbance and slope, which can visually check the bus signal quality and avoid the risk of signal transmission failure.

4. Bus fault simulation, quickly locate faults
ZPS-CANFD bus analyzer supports one-key setting of device connection, which can realize real-time adjustment of baud rate, sampling point and terminal resistance. ZPS-CANFD provides adjustment of bus resistance/capacitive load/short circuit/cable incorrect connection, analog application The communication situation of the environmental bus under the influence of load changes and connection abnormalities.
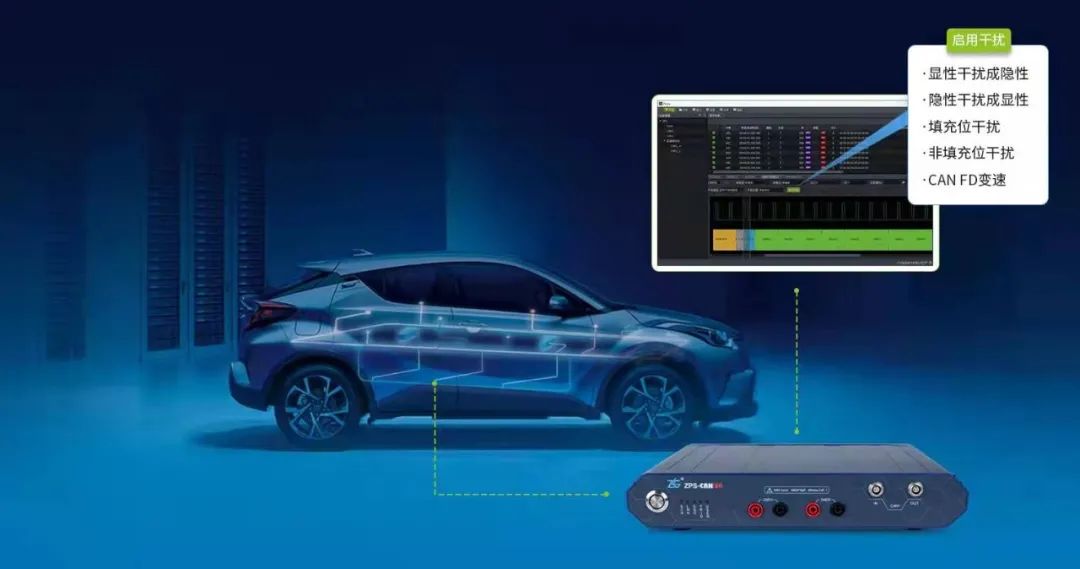
5. Robustness test
The ZPS-CANFD analyzer supports the bit-by-bit interference capability of CANFD frame data, which can simulate the bus disturbance to the maximum extent and provide the consistency test capability at the controller level. It is the best solution to verify the robustness of nodes!

Summarize
With the rapid development of automotive electronics, rail transit and other industries, CAN FD is widely used because of its outstanding real-time performance and reliability. More and more users need to perform effective data analysis on the on-site CAN FD. Through the ZPS-CANFD bus analyzer, the CAN FD data can be effectively analyzed in real time, which is helpful for fault analysis after the event, and then solves the problems existing in the CAN FD bus. This effectively improves the reliability of the vehicle network.
Source: ZLG Zhiyuan Instrument
The Links: LM32P073 GP377R-TC11-24V