“Measure the signal waveform of the common-mode voltage to the ground. If the measuring instrument or measuring method is not correct, it will affect the measurement result in the slightest, and endanger the safety of life and property. This article uses two typical examples to illustrate the impact of improper measurement methods on the results and possible safety issues, and propose correct measurement methods.
“
Abstract: Measure the signal waveform of a common-mode voltage to the ground. If the measuring instrument or measuring method is incorrect, the measurement result will be affected at the slightest, and the safety of life and property will be endangered. This article uses two typical examples to illustrate the impact of improper measurement methods on the results and possible safety issues, and propose correct measurement methods.
1. Example 1
The customer’s product is a piezoelectric ceramic and its driving Circuit. Figure 1 is the product principle and test connection diagram. The switch tube is turned on and off at a frequency of about 100kHz. The tapped Inductor realizes the boost function to drive the piezoelectric ceramic chip. The sexual load forms a resonance to make the switch tube in a soft switching state.

Figure 1 Principle and measurement connection of piezoelectric ceramic driver
Customers use our oscilloscope and single-ended passive probe to observe the voltage waveform at both ends of the load RL. The positive end (tip) and negative end (ground clamp) of the probe are respectively connected to Vo+ and Vo- of the circuit, and the circuit uses an isolated adjustable power supply. It was found that when the oscilloscope probe was connected, the working current of the circuit increased a lot, and the customer suspected that there was a problem with our oscilloscope. We built the same test system to measure the customer’s products, and found that the current displayed by the adjustable power supply after the probe was connected increased from about 100mA to more than 6 times the original value. I changed a foreign brand oscilloscope to a comparative test and found that the same problem exists.
The reason is, as shown in Figure 1, the adjustable power supply actually has capacitance to the protective grounding wire PE, which is called Ciso below, and the negative end of the oscilloscope probe is connected to PE. At high frequencies, the negative end of the probe → PE → Ciso →GND forms a low impedance path. Both Vo+ and Vo- of the circuit have a voltage of 100kHz to GND. No matter the negative terminal of the probe is connected to Vo+ or Vo-, additional current will be generated through the negative terminal of the probe → PE → Ciso → GND, generating heat on the resistance of the inductor and the loop resistance , The power supply current is increased, and the parallel low-impedance channel changes the resonance state of the driver. So it’s not the oscilloscope’s problem, but the incorrect measurement method.
Generally, people may have some misunderstandings about the isolated power supply. They think it is “completely isolated”, and often only see the isolated resistance and ignore the reactance. In fact, the isolated power supply supplied by the mains has parasitic capacitance to the ground. The source is the parasitic capacitance between the primary and secondary windings of the transformer, and the space capacitance of the secondary circuit to the chassis. Especially in order to meet the EMC standards, it is sometimes connected between the secondary and PE. Y capacitor of a certain capacity. The so-called “isolation” of isolated power supply means to provide the insulation requirements required for safe operation, and to ensure that there is a sufficiently high isolation impedance under DC and power frequency. However, the parasitic capacitance and the deliberately added capacitive reactance are reduced at high frequencies, and the isolation is reduced.
The measured output capacitance of a certain brand of adjustable power supply used in the above test to PE is 73nF, and the ground impedance of the isolated power supply is about 21.8Ω under a 100kHz sine wave.
You might think of cutting off the ground wire of the oscilloscope’s power supply to make the oscilloscope float. The test results show that the amplitude of the current increase is reduced, but the error still exists. Because in the oscilloscope, the case and the L and N lines are connected with Y capacitors to suppress EMI. Externally, some electrical appliances on the power supply line also have indirect Y capacitors between L and N to PE, and the N line is connected to the ground at the transformer. Therefore, the impedance of L and N to PE is not particularly large. After cutting off the power supply ground wire of the oscilloscope, the common mode current path is: probe negative terminal → oscilloscope EMC filter (Y capacitor, common mode inductance) → L and N lines → on the power supply line L, N to PE impedance→Ciso→GND. On the other hand, from the perspective of safe use of equipment, it is not advisable to cut off the power supply ground wire of the oscilloscope, as shown in Example 2.
2. Example 2
It is not possible to directly use a combination of a single-ended passive probe and a general-purpose oscilloscope to measure the line connected to the power grid. A common example is to measure the waveform of the primary related circuit of a switching power supply connected to the mains.
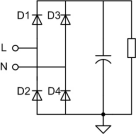
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of switching power supply rectification and filtering principle
Figure 2 is a typical rectifier filter circuit at the input of a switching power supply. In the half cycle when L is positive to N, D1 and D4 are turned on, and the primary ground potential is close to the voltage of the N line to the ground, and in the half cycle when L is negative to N, D3 and D2 are turned on, and D2 is equivalent to connecting the primary ground to the L line. Therefore, if the ground clip of the oscilloscope probe is connected to the primary ground, and the L wire is short-circuited to the ground during the half-cycle when L is negative to N, the power grid has a large enough capacity, which will cause serious accidents such as line and equipment burnout. For this reason, some people disconnect the oscilloscope’s power supply ground wire for measurement to avoid short Circuits, but this method is wrong and absolutely undesirable. The general-purpose oscilloscope is designed according to the grounding situation. When connected to a device that has a higher common-mode voltage to the ground, the exposed metal parts of the oscilloscope will be charged! It will endanger the safety of life and property, and it is also explained in the safety-related chapters of the instrument manual. The user should read the manual of the equipment and use it in the correct way.
Three, the correct measurement method
The characteristics of the measured signals in Examples 1 and 2 are that there is a common-mode voltage to the ground, and the source impedance of the common-mode voltage to the ground is low at the observed frequency. But the single-ended probe and the general-purpose oscilloscope are connected to the ground, so if they are directly connected to the measurement, the results will be affected at least, as in Example 1, or accidents, as in Example 2. The correct measurement method should be as follows:
(1) Similar to the case of Example 1, there is no potential difference between the reference ground of the circuit and the earth. To measure the voltage between two points in the circuit that is not reference ground, you can use the ZDS4000 series oscilloscope to connect two single-ended passive probes, and the negative terminal is connected to the reference ground. The positive terminal is connected to the two points to be measured, and the voltage between the two points to be measured can be obtained by using the subtraction function of Math. This method can be used for CAT O occasions, but it is not suitable for measuring lines connected to the power grid.
(2) Similar to the case of Example 1, using the ZDL6000 oscilloscope with an isolated high-speed voltage acquisition card, the capacitance of each channel to the ground is less than 80pF. In the case where the capacitance has negligible impact on the system under test, the single-ended The source probe is connected to the two points to be measured. Figure 3 uses this method to measure the waveform of RL in Example 1.

Figure 3 Waveforms at both ends of RL measured by ZDL6000
(3) Similar to the case of Example 2, the ZP1500D high-voltage differential probe and ZDS4000 series oscilloscope can be used for measurement. ZP1500D can be used in 1000V CAT II or 600V CAT III occasions.
(4) Similar to the case of Example 2, the ZDL6000 oscilloscope recorder can be used with multiple isolated high-speed voltage acquisition cards, and the matching safety probe can be used in 1000V CAT II occasions, especially for applications that need to measure multiple signals of different ground potentials at the same time . For example, in the switching power supply, the voltage between the incoming line LN, the primary filter capacitor, the transformer primary, the secondary, and the secondary filter capacitor can be measured at the same time.
The Links: LQ104V1DG83 LTM150XH-L04