This week, Counterpoint Research gave the top list of global wafer foundries sorted by mature process (node ≥40nm) capacity, as shown in the figure below.
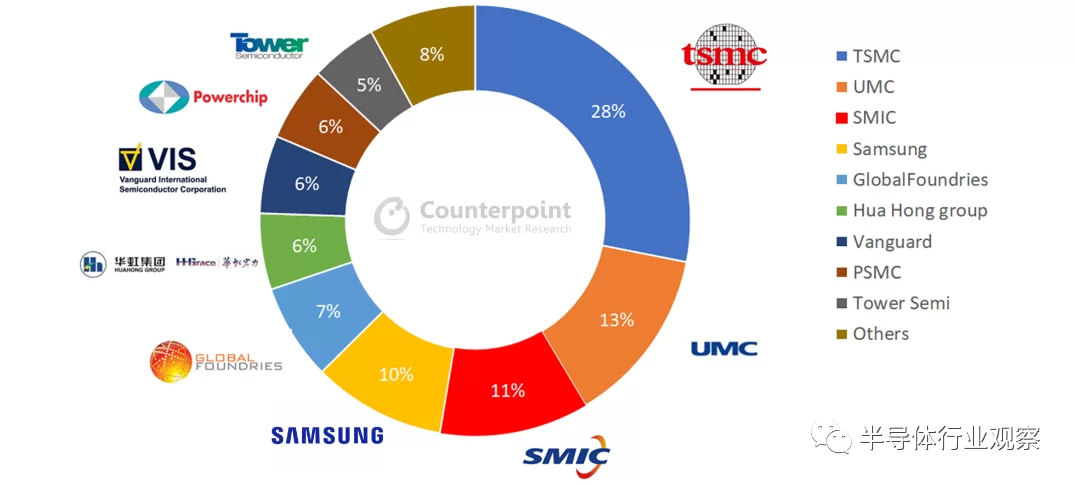
It can be seen that the top four manufacturers are: TSMC (28% market share), UMC (13%), SMIC (11%), and Samsung (10%).
The mature process is very popular in 2020, and there is a serious shortage of production capacity, which brings huge business opportunities to major wafer foundries. Judging from the industrial development situation in 2021, this shortage will be difficult to alleviate in the near future. In this regard, Counterpoint Research believes that in 2021, the mature processes of the top foundries will only be allocated to specific applications. For example, even with strong demand for 8-inch wafers, UMC announced that 8-inch wafer production capacity will only expand by 1%-3% in 2021. SMIC, which accounts for about 10% of the global mature process capacity, is also full of uncertainties in capacity expansion due to the restriction of the US ban. Overall, this wave of capacity shortages is a structural problem that will not ease until all supply chains are restocked in 2022.
The process technology is not the more advanced the better
At present, the development of semiconductor process technology shows two major trends: one is to continue to pursue advanced processes, typical representatives are TSMC, Samsung, Intel, and SMIC; the other is to focus on characteristic processes to meet diverse needs, and representative manufacturers have UMC , GF, World Advanced, Huahong Grace, etc.
Compared with mature processes, advanced processes have shortcomings. First, the cost of upstream IC design is getting higher and higher. Advanced processes can provide a good power consumption ratio for the chip, but the growth rate of its intergenerational design cost is getting higher and higher. For example, the cost of designing a 7nm chip exceeds 300 million US dollars. Huawei Kirin The 980 chip is manufactured with TSMC’s 7nm process. The Kirin 980 was successfully applied after a team of more than 1,000 engineers took 3 years and experienced more than 5,000 engineering verifications.
According to IBS’s calculations, if the NVIDIA GPU is developed based on 3nm, the cost will be as high as 1.5 billion US dollars. From the perspective of economic benefits of chip design, 7nm is a long-term node, and it is difficult to achieve a balance between PPA and cost of 5nm/3nm, unless there is an excess shipment to share the cost.
Advantages of mature processes
The mature process is mainly used to manufacture small and medium-capacity memory chips, analog chips, MCUs, power management (PMIC), analog-digital hybrids, sensors, and radio frequency chips. At the application level, the rapid growth in demand for cloud computing and 5G RF devices has provided a strong impetus for mature processes.
The wafer foundry industry is developing in a more subdivided direction. Unlike TSMC and Samsung chasing advanced processes, UMC, GF, TowerJazz, World Advanced, Huahong Grace, etc. pay more attention to the characteristic processes they are good at. Investment in mature technology improves product cost performance and competitiveness.
From the demand side, the market application prospect of characteristic technology is broad, and it has the foundation to attract more enterprises to become better and stronger in their own characteristic fields. At present, the three major types of chips, MCU, analog Circuits and discrete devices, account for nearly 50% of the overall market share, and their development is more stable, providing a foundation for characteristic process applications. What is more noteworthy is that compared with advanced processes, the penetration rate of characteristic processes in the foundry business model is relatively low. In terms of traditional logic devices, except for Intel, major manufacturers basically adopt “design-foundry-packaging and testing”. However, in the fields of analog devices, MCUs, and discrete devices, IDM’s own production is still the mainstay. This makes more room for the expansion of the foundry business of mature process technology.
In addition, the volatility of the profitability of suppliers of special processes is relatively small. On the one hand, the stability of the demand side makes the manufacturers more predictable in terms of operation and management. On the other hand, due to the relatively high maturity of the process , In terms of equipment expenditure and R&D investment scale, characteristic process manufacturers are relatively small, giving them an advantage in cost control.
What are the mature manufacturing processes? Specifically, it mainly includes the following.
Driver IC: With the increase in the penetration rate of OLED panels, the market share of OLED manufacturers has increased, while the traditional OLED DDIC is mainly based on the 80nm and above process, and the increase in its order volume has increased the production capacity of higher process nodes.
Power management chips: Benefiting from the advancement of 5G, the number of mobile phones has increased significantly, and the use of fast charging chips has gradually increased. In addition, the launch of new products such as TWS headphones has also driven the demand for power management chips and NOR Flash. The traditional PMIC process node is 0.18μm / 0.11μm, and the rising market demand provides the impetus for this mature process and the corresponding characteristic process requirements.
Sensors: The number of mobile phone cameras continues to increase. Among them, the supporting low-pixel CIS drives the demand for process nodes such as 0.18μm, and the ordinary high-pixel CIS only needs a 55nm process node, which further stimulates the demand for mature process foundries. In terms of fingerprint recognition, the under-screen optics, capacitive side, ultrasonic, etc. in the mobile phone field have gradually penetrated into the fields of smart home, finance, automobile, etc. Most of these products use the 0.11μm/0.18μm process, and the corresponding mature process and characteristic process platform will become more and more. increasingly popular.
Representative enterprise
Driven by market demand, wafer foundries that master mature processes can rely on capacity adjustment and expansion to increase their market share, especially in East Asia represented by China, where demand grows the fastest. Manufacturers such as SMIC, UMC, World Advanced, TowerJazz, etc., which are based on mature process OEMs, basically focus on discrete devices, driver ICs, PMICs and eNVMs. In addition, although TSMC and Samsung are mainly based on advanced processes, due to their large size and taking into account mature processes at the same time, they also occupy an advantageous position in the mature process market, especially TSMC, whether it is global The overall ranking of wafer foundry, or the list of mature processes, the company is in a leading position.
For SMIC, mature processes are the company’s main source of revenue. Taking the first half of 2020 as an example, 0.15μm/0.18μm, 55nm/65nm and 40nm/45nm contributed 33.4%, 32.6% and 14.9% of its revenue, respectively.
SMIC has developed a variety of characteristic process platforms, such as power/analog, high voltage drive, eNVM, mixed signal/RF, image sensor, etc. Among them, the power/analog technology is based on the existing low-power logic process platform, which can provide module architecture and medium-voltage and high-voltage devices. The high-voltage drive technology platform covers 0.15μm, 55nm, 40nm, etc.; the eNVM technology platform covers 0.35μm to The 40nm technology node features low power consumption and outstanding durability.
In terms of TSMC, it can be seen from the company’s fourth quarter 2020 financial report that 40nm/45nm revenue accounted for 8% of total revenue, 65nm accounted for 5%, 90nm accounted for 2%, 0.11μm/0.13μm accounted for 3%, 0.15μm /0.18μm accounted for 7%, 0.25μm and above accounted for 1%. In this way, TSMC’s consolidated revenue from mature processes in the quarter accounted for 26% of total revenue, which is still a considerable number.
From the perspective of historical development, TSMC began to transition from low-end wafer manufacturing based on 0.11μm+ process to wafer manufacturing based on more advanced process technology of 40nm-90nm in 2004, and started from the end of 2011. Low-end-based wafer manufacturing transitions to wafer manufacturing based on 28nm and more advanced process technology.
Samsung currently has four production lines, including three 12-inch and one 8-inch, 12-inch wafer foundry lines are distributed in South Korea and the United States, mainly for relatively high-end process technology, including 65nm, 45nm, 32/28nm HKMG, 14nm FinFET process. The 8-inch foundry line was opened in 2016, covering 180nm to 65nm nodes, mainly used for eFlash, power devices, CIS, and high-voltage processes.
In terms of UMC, due to the continuous influx of foundry orders for driver IC, PMIC, RF, IoT applications, etc., UMC’s 8-inch wafer production capacity is fully loaded. Not only that, it is reported that its production capacity in the first half of 2021 has also been fully loaded.
UMC is the first wafer foundry in the industry to announce the abandonment of 10nm and more advanced process technology. In July 2017, the company launched the dual CEO system. Within a year after that, they conducted a meticulous research on the market, and a year later, in July 2018, announced that they would focus on mature processes, while No longer invest in R&D for 10nm and more advanced processes.
Specifically, whether it is an 8-inch or 12-inch fab, UMC has focused on various new special processes, especially for the Internet of Things, 5G and automotive electronics, which have huge market and development prospects in the future. Application areas, such as UMC’s automotive electronics business, have seen annual growth rates exceeding 30% in the past few years. Including RF, MEMS, LCD driver chips, OLED driver chips and other fields, UMC has targeted strengthening technologies and has been increasing its market share.
In terms of special processes, the market has a large demand for LCD driver chips and OLED driver chips. Most of them use 80nm and 40nm processes. On this basis, UMC has imported these chips into 28nm. , UMC is also continuing to develop.
Steady and bright development prospects
The market has an urgent demand for mature process technology, and major wafer foundries also attach great importance to this business, and the industry is generally optimistic about its development prospects.
IC Insights’ Global Wafer Capacity 2020-2024 report argues that as chip feature size scaling continues to slow, chip designers are finding it increasingly difficult to justify higher costs. As a result, the pros and cons between advanced and mature processes have become clearer, and the processes used by different companies have become more targeted. This leaves room for various processes to demonstrate their own advantages.
Under such a development trend, according to the statistics and forecasts of IC Insights, the market share of various semiconductor processes is developing in a relatively more balanced direction, as shown in the figure below.
As can be seen from the figure, the proportion of mature processes of 40nm and above has not changed significantly in these years, and the market size is considerable.
For mature processes above 40nm, whether it is below 180nm or above 180nm, the market share is very stable. This is why many foundries have long focused on mature processes without investing too much capital and energy into advanced processes. At the same time, it is also the main reason why GF and UMC gave up the most advanced processes. No matter how advanced manufacturing processes develop, the market for mature manufacturing processes will still be very broad in the future and will still have good investment value.
The Links: 1MBI300L-120 LM641836